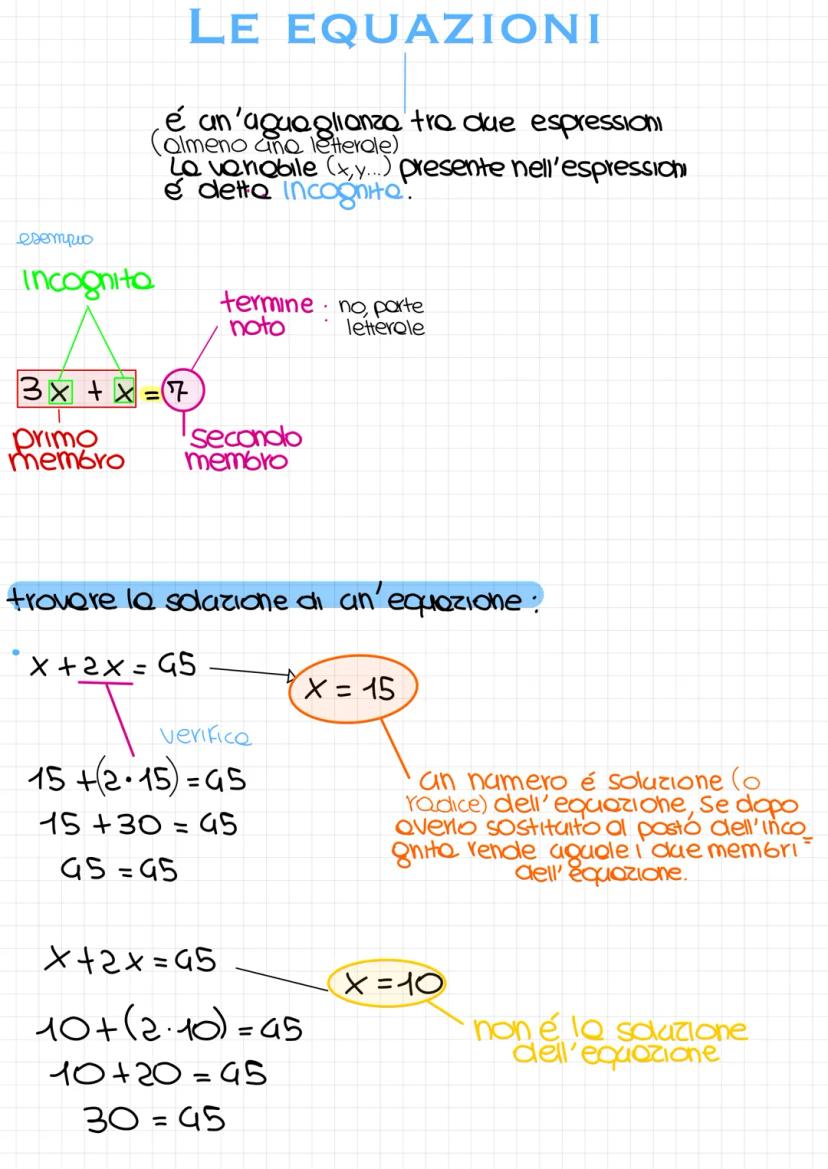
First-degree equationsform the foundation of algebraic problem-solving, teaching students... Mostra di più
Iscriviti per mostrare il contenutoÈ gratis!
Accesso a tutti i documenti
Migliora i tuoi voti
Unisciti a milioni di studenti
Iscrivendosi si accettano i Termini di servizio e la Informativa sulla privacy.